New research by geoscientists Dr Lucía Pérez Díaz, from the Department of Earth Sciences at Royal Holloway, University of London and Dr Graeme Eagles, Alfred Wegener Institute illustrates the separation of Africa and South America and subsequent deepening of what we now know as the South Atlantic ocean.

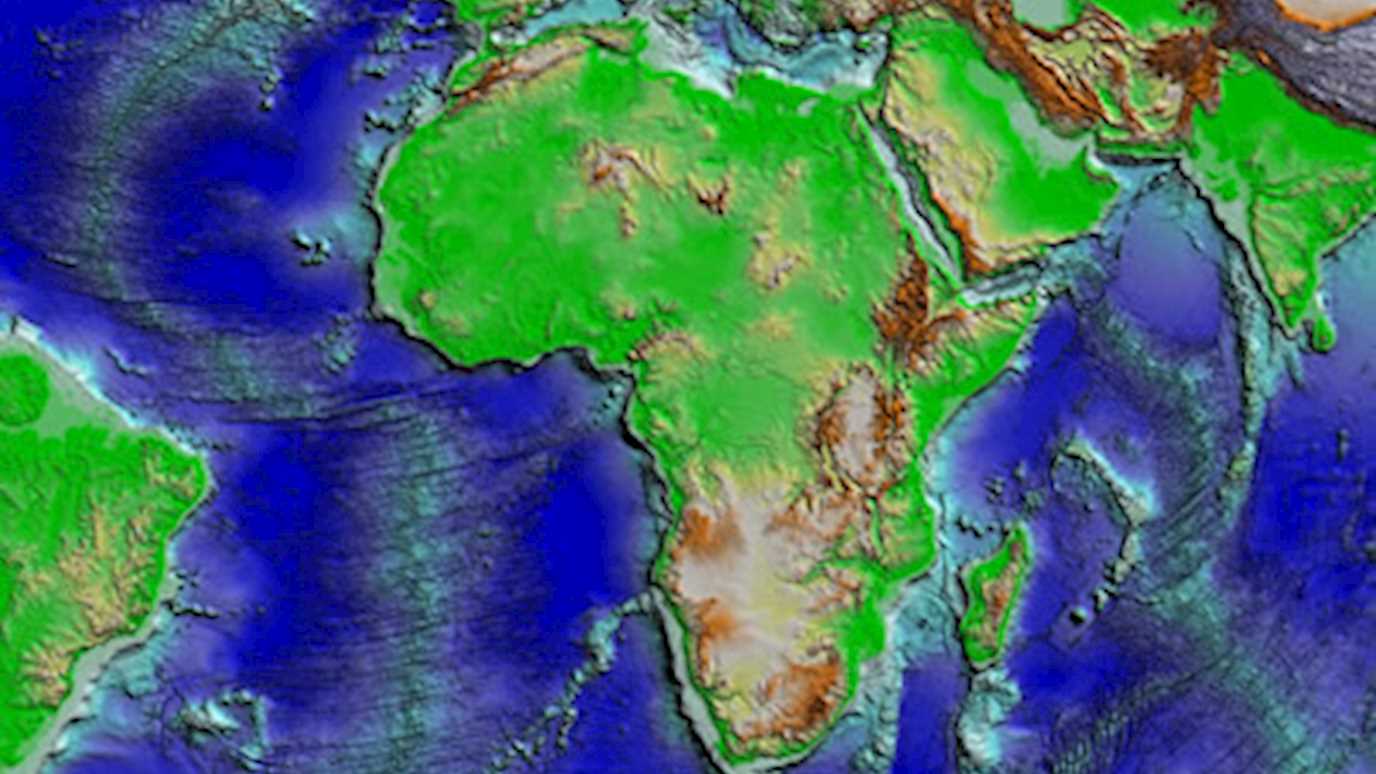
Figure caption: Reconstruction showing the positions of South America and Africa and South Atlantic depths 60 million years ago.
Their findings, published today by Nature’s Scientific Reports, reveal a series of oceanic and tectonic events that acted as triggers for global changes in climate.
In a series of computer-generated reconstructions created with equipment at Royal Holloway, they show how continental separation began in the south, between the tip of Argentina and South Africa, progressing northwards over millions of years. Their reconstructions also shed light on the impact of tectonic events on the formation and circulation of water masses. This is of crucial importance because ocean dynamics are known to have a direct impact on the Earth’s climate.
Dr Pérez Díaz comments,
“This research is a big step forward from previous attempts, which were done in sketch form owing to the quality of the datasets available at the time and limited knowledge about many of the processes active during continental separation. With these new reconstructions as the starting point, there are exciting possibilities to further investigate past global water circulation paths and the Earth’s paleoclimate, and their relation to plate tectonic motions.”
The research reveals that the circulation of water between the South and North Atlantic, shown in reconstructions to become possible in the period between 100-80 million years ago, provides an explanation for previously suggested changes in climatic conditions at that time. Further opening and deepening of connections between the Earth’s major oceans in more recent times (35-30 million years ago) may have triggered a period of cooler climate and subsequent development of ice sheets in Antarctica.
The similarities between the continental coastlines of Africa and South America were noted by map makers as early as the 16th century. The thought that these two continents could have been one single landmass in the past would play a fundamental role in the development and consolidation of plate tectonic theory in the mid-60s. Since then, the South Atlantic has been the focus of much research aiming to unravel the complex series of motions through which the African and South American plates have reached their present-day configuration. These two plates started diverging sometime around 130 million years ago, and continue to do so today. As they move apart, molten lava from the Earth’s mantle erupts between them, cooling in contact with seawater and forming new oceanic crust along what we know as the South Atlantic mid-ocean ridge.
This research was funded by the COMPASS Consortium and carried out as part of the Continental Margins Research Group at the Department of Earth Sciences at Royal Holloway. Dr Pérez-Díaz is currently working with the Fault Dynamics Research Group (also at Royal Holloway) studying the evolution of continental margins during the break-up of continents in the Earth’s past, and implications for oil and gas exploration.
The Department of Earth Sciences has earned a reputation as one of the leading centres for Earth Science in the UK. The highly respected MSc and PhD teaching and research activities help maintain vital links with industrial and commerial partners, providing research support and employment opportunities for graduates.